Small-Space Aquaponics: How to Grow More with Less
The burgeoning interest in sustainable food production has driven a significant increase in the adoption of aquaponics, a symbiotic system integrating aquaculture (raising aquatic animals) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil). While traditionally associated with larger-scale operations, the inherent flexibility of aquaponics makes it remarkably adaptable to small spaces, offering urban dwellers and those with limited land access the opportunity to cultivate fresh produce and raise fish concurrently. This article explores the principles and practical considerations for successfully implementing a small-space aquaponics system, maximizing yield and efficiency within constrained environments.
Understanding the Symbiotic Relationship
Aquaponics hinges on the mutually beneficial relationship between fish and plants. Fish waste, rich in ammonia, is processed by beneficial bacteria residing in the system's biofilter. These bacteria convert ammonia, toxic to both fish and plants, into nitrite, and subsequently into nitrate, a readily absorbable form of nitrogen for plants. The plants, in turn, filter the water, removing excess nutrients and providing a cleaner environment for the fish. This closed-loop system minimizes water usage and waste, a key advantage particularly in areas with limited water resources.
Key Components of a Small-Space Aquaponics System
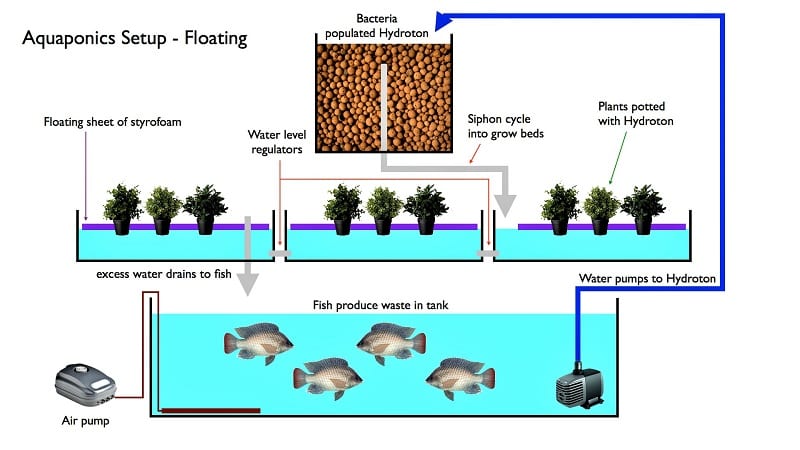
Regardless of scale, a successful aquaponics system requires several essential components:
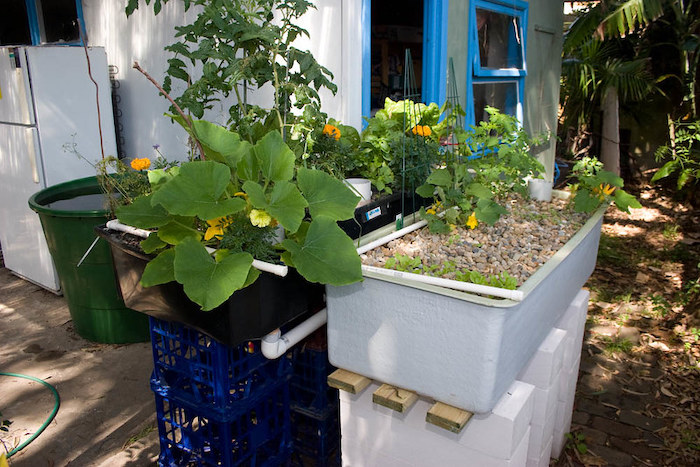
- Fish Tank: This serves as the habitat for the fish, typically tilapia, catfish, or goldfish, chosen for their hardiness and suitability for aquaponics. The size will depend on the number of fish and the overall system design. For small spaces, a relatively shallow, wide tank may be preferable to a tall, narrow one.
- Grow Bed: This is where the plants are cultivated. Options include media beds (using gravel, clay pebbles, or other inert materials) or deep water culture (DWC) systems, where the plant roots hang in nutrient-rich water. Media beds are generally preferred for beginners due to their relative simplicity and robustness. The grow bed should be sized proportionally to the fish tank and the anticipated plant growth.
- Biofilter: The heart of the system, the biofilter houses the beneficial nitrifying bacteria crucial for ammonia conversion. This can be integrated into the grow bed itself (e.g., a media bed acts as a biofilter) or housed separately, utilizing materials like lava rock, bioballs, or other porous media that offer ample surface area for bacterial colonization. The efficiency of the biofilter directly impacts the health of both fish and plants.
- Pump: A submersible pump circulates water from the fish tank through the biofilter and then to the grow bed, ensuring continuous nutrient delivery to the plants and oxygenation for the fish. Selecting a pump with appropriate flow rate is critical to maintaining system balance.
- Water Reservoir/ Sump Tank: This acts as a reservoir for the circulated water and helps regulate water level fluctuations. It often houses the pump and can provide additional space for the biofilter.
System Design Considerations for Small Spaces
Adapting aquaponics to small spaces necessitates careful planning and consideration of several factors:
Space Optimization
Verticality is key. Utilizing vertical space through stacked systems, wall-mounted grow beds, or tower systems can dramatically increase plant yield within a limited footprint. Consider using shelves or repurposing furniture to create vertical growing space. Even a small balcony can accommodate a productive aquaponics setup with creative design.
System Size and Scaling
Begin small. Starting with a smaller system allows you to gain experience and troubleshoot potential issues before scaling up. A 10-20 gallon fish tank, coupled with a correspondingly sized grow bed, is a good starting point for beginners. As your confidence and expertise grow, you can expand your system.
Choosing the Right Plants and Fish
Select plants and fish species appropriate for the system's size and environmental conditions. Fast-growing, leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and basil are excellent choices for small aquaponics systems, as they require less space and mature quickly. Hardy fish species like tilapia or certain types of goldfish are suitable for beginners due to their adaptability and tolerance to less-than-ideal conditions. Avoid overcrowding the fish tank, which can lead to increased ammonia levels and compromised water quality.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring is crucial for the health and productivity of a small-space aquaponics system. Parameters such as water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels must be checked regularly using appropriate testing kits. Maintaining optimal water quality is paramount to the success of the system. Regular cleaning of the system, including removing debris from the grow bed and occasional water changes, is essential to prevent buildup of waste and maintain a healthy environment.
Advanced Techniques for Enhanced Productivity
While basic aquaponics principles provide a foundation for successful small-scale cultivation, incorporating advanced techniques can further enhance yield and efficiency:
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT systems are highly efficient, using a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over the plant roots. They are well-suited for small spaces due to their compact design, allowing for a high plant density within a limited area. This method requires precise control of water flow to ensure sufficient nutrient delivery without causing root rot.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
DWC involves suspending plant roots in aerated nutrient solution. This method is particularly effective for fast-growing, leafy greens. DWC systems require careful monitoring of oxygen levels and nutrient solution to avoid problems like root rot or nutrient deficiencies.
Automated Systems
For increased convenience and improved consistency, incorporating automated systems for tasks such as water level control, temperature regulation, and nutrient dosing can significantly enhance the efficiency of a small-space aquaponics setup. Automated systems can be more expensive upfront, but they can save time and effort in the long run.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful planning and diligent maintenance, small-space aquaponics systems may encounter challenges. Recognizing and addressing these issues promptly is crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive system:
- High Ammonia Levels: Indicates insufficient biofiltration or fish overstocking. Address this by increasing biofilter capacity or reducing the number of fish.
- Low Dissolved Oxygen: Can lead to fish stress and death. Increase aeration by adding an air pump or increasing water circulation.
- Algal Blooms: Excessive light or nutrient buildup can trigger algal blooms. Reduce light intensity or address nutrient imbalances.
- Plant Nutrient Deficiencies: Manifest as yellowing or stunted plant growth. Test the nutrient solution and adjust accordingly.
- Disease Outbreaks: Maintain good hygiene and monitor fish and plants for signs of disease. Address any issues promptly to prevent wider spread.
In conclusion, small-space aquaponics presents a compelling solution for individuals seeking sustainable, space-efficient food production. With careful planning, appropriate system design, and diligent monitoring, even limited spaces can yield a bountiful harvest of fresh produce and healthy fish, fostering a rewarding and environmentally conscious lifestyle.